CCM Tablet
₹ 231.10 ₹ 215.00 price_including_tax
A Bottle of 30 Tablet Each Contains
Calcium Citrate maleate, Vitamin D3, Folic Acid,
Glaxo SmithKline Pharma Ltd
CCM Tablet

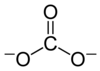 Lewis structure of Carbonate,
Lewis structure of Carbonate, in Calcium Carbonate
in Calcium Carbonate
Uses of CCM Tablet
CCM; as a calcium supplement. Hence as diet supplements.
How it Work
Calcium carbonate is medicinal as an inexpensive dietary calcium supplement for a gastric antacid. It may be used as a phosphate binder for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia (primarily in patients with chronic renal failure).
Common Side Effects
Common side effects include; excessive consumption can be hazardous. vomiting, abdominal pain, altered mental status, renal failure, alkalosis, and hypercalcemia, mostly in men with peptic ulcer disease. These adverse effects can be reversed when the regimen quit.
Moreover,
Click Here To Search More Substitute
*Follow your doctor’s advice.
*Always take medicine after food.
*Take the medicine with water.
Fast Fact
Excess calcium from supplements, fortified food, and high-calcium diets, can cause milk-alkali syndrome,
Calcination of limestone using charcoal fires to produce quicklime has been practiced since antiquity by cultures all over the world.
Frequently Asked Question
Raw Milk. Broccoli, Cheese, Yogurt.
Calcium supplements are intended to be consumed with a meal, and when taken as directed, the two forms of calcium are absorbed in roughly the same rate. However, when taken on an empty stomach, the body has a much easier time absorbing calcium in its citrate form vs. its carbonate form.
Phosphorous: Also known as phosphoric acid and phosphate, phosphorous, which is in cola and many processed foods, can interfere with calcium absorption. Insoluble fiber: This type of fiber, such as the kind in wheat bran, reduces calcium absorption.
Food Sources; Milk and milk products.
Solubility and Stability of Vitamins
| Vitamin | Soluble in Water | Stable to Air Exposure | Stable to Light Exposure | Stable to Heat Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | no | partially | partially | relatively stable |
| Vitamin C | very unstable | yes | yes | yes |
| Vitamin D | no | no | no | no |
| Vitamin E | no | yes | yes | no |
| Vitamin K | no | no | yes | no |
| Thiamine (B1) | highly | no | Ξ | > 100 °C |
| Riboflavin (B2) | slightly | no | in solution | no |
| Niacin (B3) | yes | no | no | no |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | quite stable | Ξ | no | yes |
| Vitamin B6 | yes | Ξ | yes | Ξ |
| Biotin (B7) | somewhat | Ξ | Ξ | no |
| Folic Acid (B9) | yes | Ξ | when dry | at high temp |
| Vitamin B12 | yes | Ξ | yes | no |
Be the first to review “CCM Tablet” Cancel reply
Related products
Metoprolol and Hydrochlorothiazide
Metoprolol and Hydrochlorothiazide
Methylcobalamin Mecobalamin






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.